Section “Male Only”: Male Hormone Support
Anatomy and Physiology
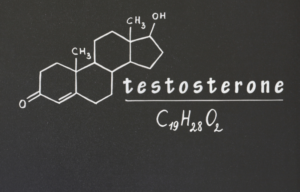
This section delves into the intricacies of male hormones, emphasizing the role of the endocrine system in regulating reproductive health and overall vitality. Key components include the testes, which produce testosterone, and the hypothalamus-pituitary-testicular axis, a complex hormonal interplay governing male reproductive functions.
Importance to Overall Health
Male hormone support is critical for overall health, influencing not only reproductive functions but also energy levels, muscle mass, and bone density. Balanced testosterone levels contribute to vitality, sexual health, and the maintenance of various physiological processes throughout different life stages.
Dysfunction
Male hormone imbalances can lead to conditions such as hypogonadism, erectile dysfunction, and reduced libido. Recognizing signs of hormonal dysfunction, including fatigue, changes in mood, and sexual health issues, is crucial for implementing targeted interventions.
Nutritional Component
The nutritional biochemistry of male hormone support focuses on optimizing the endocrine system, particularly addressing the regulation of testosterone and other hormones crucial for male reproductive health. Key pathways include hormone synthesis, metabolism, and the balance necessary for maintaining vitality and overall well-being.
- Testosterone Synthesis: Nutrients play a critical role in the synthesis of testosterone, a key male sex hormone. Factors such as amino acids, vitamins, and minerals contribute to the regulation of testosterone levels.
- Sperm Health: Certain nutrients are essential for the production and health of sperm, influencing male fertility. Adequate levels of antioxidants, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids support reproductive health.
- Endocrine Balance: The interplay of various nutrients influences the overall balance of male hormones, supporting vitality, energy levels, and reproductive function.
Science Behind Nutritional Influence
Nutrients and dietary choices significantly impact the nutritional biochemistry of male hormone support:
- Zinc: Crucial for testosterone synthesis and sperm health, zinc is found in foods like lean meats, nuts, and seeds.
- Vitamin D: Essential for overall hormonal balance, vitamin D is synthesized through sunlight exposure and found in fatty fish and fortified dairy products.
- Selenium: Supports sperm health and is present in foods like Brazil nuts, seafood, and whole grains.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3s may contribute to hormone balance and overall reproductive health.
- L-Arginine: An amino acid that supports blood flow and may have a positive impact on erectile function. Found in nuts, seeds, and poultry.
Supplements
Explore the potential benefits of glandular supplements tailored to your individual health profile by setting up a free 10 minute call with Dr. Kneessi. Otherwise here are some of the most common supplement recommendations for supporting this system. Glandular or organ supplements will support most of the following processes.
- Zinc: Essential for testosterone production and reproductive health.
- Vitamin D: Supports overall health and may play a role in testosterone levels.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids (Fish Oil): Supports cardiovascular health and may have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Magnesium: Important for muscle function and overall well-being.
- DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone): A precursor to testosterone, may support hormonal balance.
These supplements are chosen to provide comprehensive support for male reproductive health and hormonal balance. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with hormonal disorders or taking medications, to ensure the supplements are suitable for individual health needs and do not interfere with prescribed treatments.