Section 7c: Endocrine – Hyperpituitary
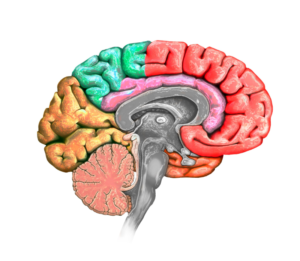
Anatomy and Physiology:
The pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland,” is a small, pea-sized structure located at the base of the brain. It plays a central role in the endocrine system by producing and releasing hormones that regulate various bodily functions. Hyperpituitarism refers to an overactivity of the pituitary gland, leading to excessive secretion of one or more hormones.
Importance to Overall Health
Maintaining proper pituitary function is crucial for hormonal balance, growth, and reproductive health. Hyperpituitarism can result in elevated levels of specific hormones, such as growth hormone (GH) or prolactin, leading to various symptoms and potential complications. Identifying and managing hyperpituitarism is essential for preventing long-term health issues and maintaining overall endocrine equilibrium.
Dysfunction
Hyperpituitarism can be caused by tumors on the pituitary gland, leading to excessive hormone production. Symptoms vary based on the hormone affected but may include rapid growth, irregular menstruation, and changes in vision. If left untreated, hyperpituitarism can lead to complications such as osteoporosis, infertility, and cardiovascular issues. Recognizing signs of hyperpituitarism is crucial for seeking medical evaluation, implementing dietary and lifestyle changes, and potentially exploring medical interventions to manage the condition and restore hormonal balance.
Nutritional Component
The nutritional biochemistry of the hyperpituitary endocrine system involves the regulation of the pituitary gland, a master gland that controls the function of other endocrine glands. The 3 most well known hormones produced by the pituitary include growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
- Growth Hormone Synthesis: The pituitary gland produces growth hormone, crucial for growth, cell repair, and metabolism. Nutrients like amino acids, obtained from protein-rich foods, play a role in growth hormone synthesis.
- TSH Regulation: The pituitary releases TSH to stimulate the thyroid gland. Nutrients such as iodine, selenium, and zinc are essential for the synthesis and function of TSH.
- ACTH Synthesis: ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol. Nutrients like vitamin C and B-vitamins support adrenal function and the synthesis of cortisol.
Science Behind Nutritional Influence
- Protein: Amino acids from protein-rich foods contribute to growth hormone synthesis, supporting overall growth and repair.
- Iodine: Essential for the synthesis of TSH, which regulates thyroid function. Iodine-rich foods include seaweed, dairy, and fish.
- Selenium and Zinc: Support the function of TSH and overall thyroid health. Dietary sources include Brazil nuts, seafood, and nuts and seeds.
- Vitamin C: Essential for adrenal function and the synthesis of ACTH. Citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers are good sources of vitamin C.
- B-Vitamins: Support adrenal function and the production of hormones. Whole grains, meat, and leafy greens are rich in B-vitamins.
Supplements
Explore the potential benefits of glandular supplements tailored to your individual health profile by setting up a free 10 minute call with Dr. Kneessi. Otherwise here are some of the most common supplement recommendations for supporting this system. Glandular or organ supplements will support most of the following processes.
- Bromelain: May help reduce inflammation and support overall pituitary health.
- Vitamin D: Essential for immune function and may play a role in regulating pituitary hormones.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Have anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit pituitary health.
- Curcumin: Known for its anti-inflammatory effects and potential support for pituitary function.
- Adaptogenic Herbs (e.g., Rhodiola): May help the body adapt to stress and support overall endocrine health.
These supplements are chosen to provide general support for individuals with potential hyperactivity of the pituitary gland. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, especially for those with endocrine disorders or taking medications, to ensure the supplements are suitable for individual health needs and do not interfere with prescribed treatments.