Section 5: Liver/Gallbladder
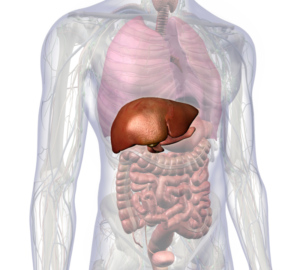
Anatomy and Physiology:
The liver and gallbladder are integral components of the digestive system, each playing distinct yet interconnected roles. The liver, the body’s largest internal organ, performs functions such as detoxification, metabolism of nutrients, and synthesis of essential proteins. The gallbladder stores and releases bile, a substance produced by the liver that aids in the digestion and absorption of fats.
Importance to Overall Health
The liver processes and filters blood, removing toxins and metabolizing nutrients for distribution to the body. The gallbladder’s release of bile aids in the breakdown of dietary fats, facilitating their absorption. Optimal liver and gallbladder function is important for digestive health, nutrient absorption, and metabolic balance.
Dysfunction
Liver and gallbladder dysfunction can manifest as conditions like fatty liver disease, gallstones, and impaired detoxification. Factors such as poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medications can contribute to dysfunction. Impaired liver function may result in toxin buildup, while gallbladder issues can lead to digestive discomfort and nutrient malabsorption. Signs of dysfunction, such as abdominal pain, jaundice, or changes in digestion are important to seek care from a doctor before implementing dietary and lifestyle interventions to support liver and gallbladder health and prevent long-term complications.
Nutritional Component
Key biochemical pathways include the metabolism of nutrients, detoxification of harmful substances, and the synthesis of bile acids essential for fat digestion.
- Detoxification Processes: The liver plays a central role in detoxifying harmful substances through enzymatic reactions, converting them into water-soluble compounds that can be excreted. Nutrients like antioxidants support these detoxification pathways.
- Bile Synthesis and Storage: Bile acids, synthesized in the liver and stored in the gallbladder, are released during meals to aid in the digestion and absorption of fats. Choline, found in foods like eggs, supports bile synthesis.
- Fat Metabolism: The liver is involved in the breakdown of fats, converting them into energy or storing them for later use. Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids support healthy fat metabolism.
Science Behind Nutritional Influence
Nutrients and dietary choices play vital roles in supporting liver and gallbladder health:
- Turmeric (Curcumin): Exhibits anti-inflammatory effects and supports liver health by aiding in detoxification processes.
- L-Glutathione: A powerful antioxidant produced in the liver, L-Glutathione supports detoxification processes.
- Amino Acids: contribute to the synthesis of molecules and enzymes that facilitate various phases of detoxification, helping the body eliminate harmful substances
Supplements
Explore the potential benefits of glandular supplements tailored to your individual health profile by setting up a free 10 minute call with Dr. Kneessi. Otherwise here are some of the most common supplement recommendations for supporting these systems.
- Milk Thistle: Known for its liver-protective properties and potential to support liver detoxification.
- Turmeric (Curcumin): Exhibits anti-inflammatory effects and may support liver health.
- Dandelion Root: Traditionally used to support liver and gallbladder function.
- Artichoke Extract: Contains compounds that may promote liver health and bile production.
- L-Glutathione: A powerful antioxidant that supports detoxification processes in the liver.
These supplements are selected to aid liver and gallbladder health. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with existing liver or gallbladder conditions, to ensure the supplements are appropriate for individual health needs and do not interact with medications.