Section 4: Cardiovascular System
Anatomy and Physiology
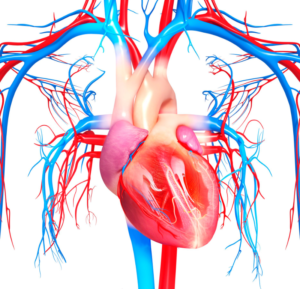
The cardiovascular system, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, plays a central role in transporting oxygen, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body. The heart serves as the muscular pump, while arteries, veins, and capillaries form an intricate network for blood circulation. The cardiac cycle, controlled by the electrical impulses in the heart, ensures rhythmic contractions and relaxations, facilitating blood flow to meet the body’s demands.
Importance to Overall Health
The cardiovascular system is paramount for maintaining overall health and homeostasis. Efficient circulation ensures oxygen and nutrient delivery to cells and removes waste products. The heart’s ability to pump blood effectively influences energy levels, organ function, and exercise capacity.
Dysfunction
Cardiovascular dysfunction can manifest as conditions like hypertension, atherosclerosis, and heart failure. Uncontrolled risk factors, such as high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels, and inflammation, contribute to these issues. Dysfunction in the cardiovascular system can lead to impaired blood flow, increased risk of clot formation, and compromised oxygen delivery to tissues. Recognizing early signs of cardiovascular issues and implementing preventive measures, including dietary and lifestyle changes, is essential for maintaining optimal heart health and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Nutritional Component
The nutritional biochemistry of the cardiovascular system involves intricate pathways that influence blood vessel function, lipid metabolism, and overall heart health. Key processes include the regulation of blood pressure, cholesterol synthesis, and the prevention of oxidative stress.
- Nitric Oxide Production: Nitric oxide, a signaling molecule, plays a crucial role in vasodilation, improving blood flow. Nutrients such as arginine, found in nuts and seeds, contribute to nitric oxide synthesis.
- Cholesterol Synthesis and Metabolism: Nutritional biochemistry influences the synthesis and metabolism of cholesterol. For instance, plant sterols found in vegetables and nuts can help lower LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels.
- Antioxidant Defense: Oxidative stress, a contributor to cardiovascular diseases, is countered by antioxidants. Vitamins C and E, present in fruits and vegetables, neutralize free radicals and protect against oxidative damage.
Science Behind Nutritional Influence
Various nutrients play essential roles in supporting cardiovascular health:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3s reduce inflammation, support arterial health, and lower the risk of cardiovascular events.
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): This antioxidant is involved in energy production within cells, including those of the heart. CoQ10 can be found in fish, meat, and whole grains.
- Garlic: Contains allicin, which may help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
Supplement
Explore the potential benefits of glandular supplements tailored to your individual health profile by setting up a free 10 minute call with Dr. Kneessi. Otherwise here are some of the most common supplement recommendations for supporting this system.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids (Fish Oil): Supports heart health by reducing inflammation and improving lipid profiles.
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): A powerful antioxidant that promotes overall cardiovascular function.
- Magnesium: Supports blood vessel health and helps regulate blood pressure.
- Garlic: May contribute to cardiovascular health by supporting healthy blood vessels.
- Hawthorn Extract: Known for its potential benefits on blood pressure and overall heart function.
These supplements are chosen to complement cardiovascular health strategies. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, especially for those with existing cardiovascular conditions or taking medications, to ensure the supplements align with individual health needs and do not pose any risks of interactions.