Introduction to Leaky Gut
Leaky gut is a term used as a simple explanation for increased intestinal permeability. Imagine your intestines as a long hose. If the hose is not damaged, then water will move freely through one end and out the other side. Now, imagine that same hose with tiny punctures. The water now leaks out before reaching its intended destination. Leaky Gut Syndrome is similar to a damaged hose, as particles can leak out into the body where they shouldn’t be. This causes damage and dysfunction resulting in poor health.
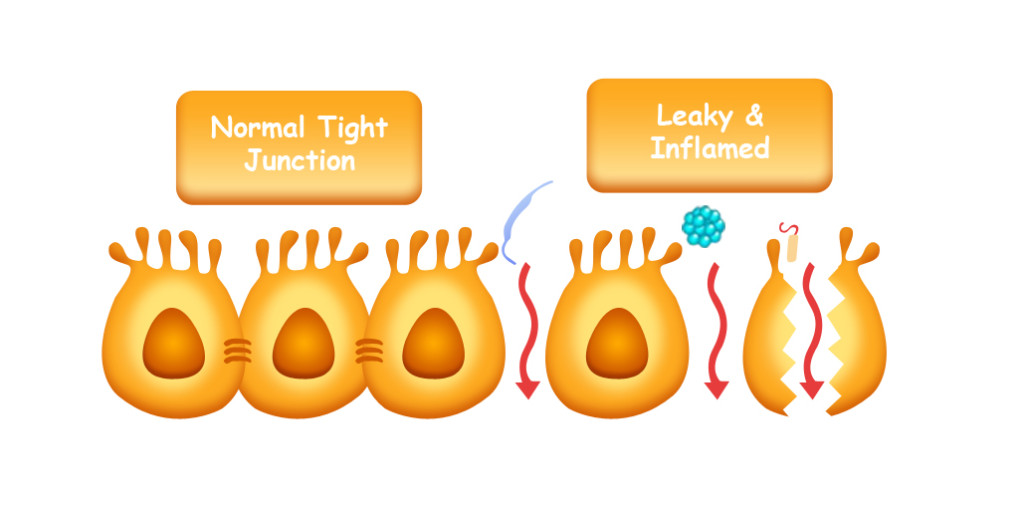
Natural & Selective Barrier
Your intestines are designed to act as a natural and selective barrier allowing nutrients in while keeping foreign objects out. With leaky gut, there is damage to this natural barrier, exposing our body’s immune system to objects it normally isn’t exposed to. A vital component of this natural barrier is a tight junction and with leaky gut, tight junctions fail. Your tight junctions are what keep out toxins, microbes, and undigested food particles from entering the circulatory system. With the rise in poor dietary choices, exposure to toxins and chemicals, heightened stress levels, and dysbiosis (bacterial imbalance), the prevalence of leaky gut has significantly increased.
Healthy Gut Function
The human digestive tract plays a vital role in breaking down food and facilitating its absorption into the bloodstream, which then transports it to the appropriate location in the body for utilization or storage. The digestive tract also serves as a critical line of defense, as it houses numerous immune cells to fight off potential threats.
In a healthy gut, small gaps in the intestinal walls facilitate the passage of water and nutrients while simultaneously blocking harmful substances. This process, known as intestinal permeability, allows for the selective transfer of substances through the intestinal walls. Problems arise when damage to these walls results in increased permeability throughout the gut. This heightened permeability can subsequently lead to widespread inflammation and trigger an immune system response.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of Leaky Gut Syndrome can vary widely depending on the individual and the severity of the condition. Some common signs/symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain and bloating
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Food sensitivities
- Skin rashes and eczema
- Joint pain and inflammation
- Fatigue and brain fog
- Anxiety and depression
- Autoimmunity
Root Cause
Leaky Gut Syndrome is caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some common causes and risk factors include:
- Poor diet high in processed foods and excess sugar
- Chronic stress and inflammation
- Infections such as SIBO (small intestine bacterial overgrowth) and candida overgrowth
- Medications such as NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), antibiotics, and acid-suppressing drugs
- Environmental toxins such as pesticides, heavy metals, and mold
- Alcohol
- Age, as gut permeability tends to increase with age


